
In the world of high-end gaming graphics cards, improvements in benchmarks like frame rate, resolution, and sharpness dominate much of the discussion. But a new driver update for Nvidia cards today also includes an important improvement that could help reduce the latency between when a player enters their input and when they see the results of that input on-screen. That's enabled by a new Ultra-Low Latency Mode that Nvidia is adding as an option in its software Control Panel through a Game Ready driver update today.
For a decade now, Nvidia's graphics drivers tried to queue an additional one-to-three frames of video ahead of time (depending on user settings). This meant that, after the next frame was ready, the GPU could use otherwise "idle" time to start processing what future frames might look like.
This frame queueing helped smooth out frame rates in cases where the system was temporarily overloaded for one reason or another, letting the GPU squeeze out a frame while the system played catch up. But this frame-rate smoothing also added additional latency, because the system was essentially working from slightly outdated inputs for a few frames.
With today's update, Nvidia lets users essentially turn that frame queue setting down to zero in the new Ultra-Low Latency mode. That means frames are generated "just in time" based on the latest available inputs, reducing latency as far as possible (but giving no room for error as far as maintaining a smooth frame rate is concerned.
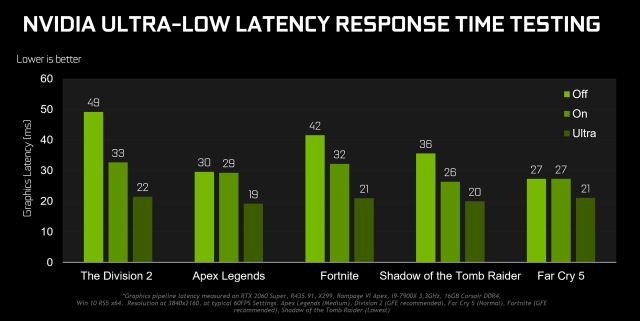
Nvidia testing in popular games running at 60fps found average graphical latency reduced anywhere from 6 to 11ms (20% to 33%) with the Ultra-Low Latency mode. That's not the kind of reduction players can necessarily perceive with the naked eye, but even that small change could improve the "feel" of the responsiveness in the twitchiest of games. Nvidia says GPU-bound games running between 60 and 100fps will see the biggest impact from the change.
Nvidia's Ultra-low Latency mode comes months after AMD started offering a similar feature, called Anti-Lag, on its RX 7700 series cards (Nvidia's Ultra-low latency mode is launching in beta for "all GPUs"). Both features are integrated directly into DirectX 9 and 11; DirectX 12 games already give developers more direct control over when to queue frames.
Nvidia's latest update also offers improvements in linear scaling (mainly for low-resolution pixel-art games), improved image quality filters, and support for new 30-bit color mode across Nvidia's product line. You can download the driver directly here or through the GeForce Experience app.
https://arstechnica.com/gaming/2019/08/new-nvidia-driver-update-cuts-latency-down-to-the-bone/Bagikan Berita Ini














0 Response to "New Nvidia driver update cuts latency down to the bone - Ars Technica"
Post a Comment